Parler
Parler Gab
Gab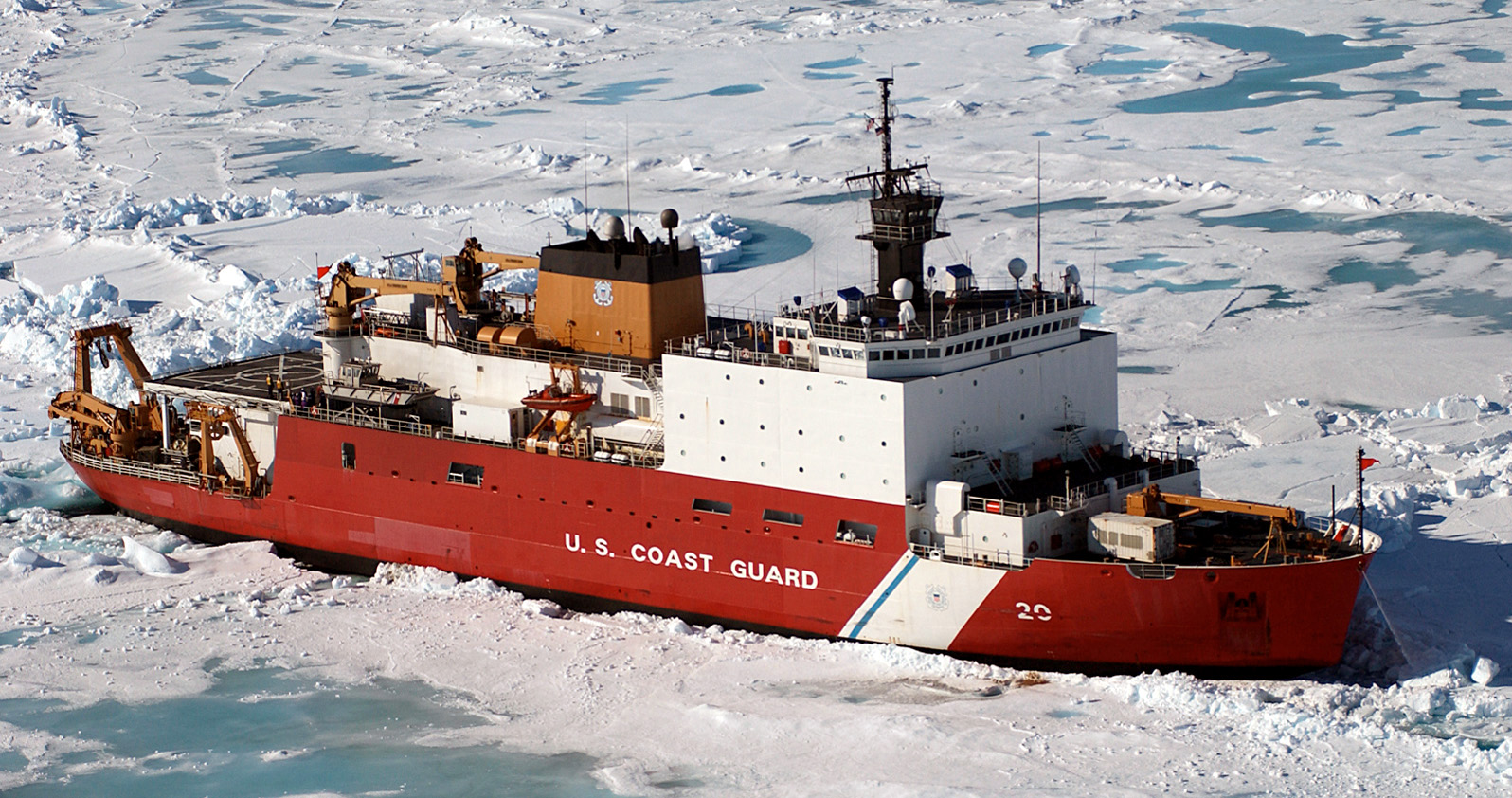
- U.S. and Finland agree to build 11 icebreakers—four in Finland, seven in the U.S.—worth $6.1 billion.
- The U.S. currently has only one operational icebreaker, while Russia boasts 40 and China expands its polar fleet.
- Melting ice opens new trade routes and resource access, making Arctic control vital for national security.
- Finland, U.S. and Canada collaborate under the Icebreaker Collaboration Effort (ICE Pact) to accelerate Arctic shipbuilding.
- Deal supports Finnish economy amid Russian sanctions and strengthens U.S. shipbuilding jobs.
The icebreaker gap: Why America is playing catch-up
For decades, Russia has dominated Arctic operations, deploying nuclear-powered icebreakers and militarizing its northern coastline. Meanwhile, China—despite having no Arctic territory—has aggressively positioned itself as a "near-Arctic" power, investing in polar research vessels and infrastructure under its "Polar Silk Road" initiative. The U.S. Coast Guard currently relies on aging ships, including the 48-year-old Polar Star, while adversaries modernize their fleets. Admiral Kevin Lunday, Acting Commandant of the Coast Guard, emphasized that without new icebreakers, America risks losing sovereignty over Arctic waters—a region rich in oil, rare earth minerals and strategic military positioning.Finland’s role: A small nation with big Arctic expertise
Finland, dubbed the "Land of a Thousand Lakes," has spent a century perfecting icebreaker technology out of necessity. Its ports freeze annually, forcing innovation in polar shipbuilding. Today, Finnish engineers design 80% of the world’s icebreakers, making them indispensable allies in the U.S. effort to reclaim Arctic influence. The deal includes four Finnish-built vessels and seven constructed in U.S. shipyards, bolstering domestic jobs while leveraging Finnish craftsmanship. Finnish Prime Minister Petteri Orpo hailed the agreement as an economic lifeline amid fallout from Russia’s war in Ukraine, stating it brings "investments, jobs and hope."The ICE Pact: A trilateral alliance for Arctic security
The agreement builds on the Icebreaker Collaboration Effort (ICE Pact), a 2024 trilateral alliance between the U.S., Canada and Finland to accelerate polar shipbuilding and share technology. The Department of Homeland Security’s Supply Chain Resilience Center (SCRC) leads U.S. coordination, ensuring industrial and military needs align. The ICE Pact is more than a shipbuilding program—it’s a geopolitical statement. By pooling resources, NATO allies aim to deter Russian and Chinese encroachment in the Arctic, safeguarding trade routes and undersea communications cables critical to global security.The bigger picture: Arctic as the new Cold War frontier
The Arctic isn’t just about icebreakers—it’s about control. Russia views the region as essential for its nuclear submarine operations, while China eyes its untapped resources to fuel its tech and energy ambitions. The U.S., late to the game, must now play catch-up or risk being sidelined in a region that could define 21st-century power dynamics. As part of the deal, Finland and the U.S. will also collaborate on quantum computing and 6G networks, signaling deeper technological and defense ties. For Trump, the agreement underscores his "peace through strength" doctrine—countering adversaries not just with rhetoric, but with strategic investments.A frozen chessboard reshapes global power
The $6 billion icebreaker deal marks a turning point in U.S. Arctic strategy. By partnering with Finland, America gains cutting-edge technology to secure its polar interests, counter Russian militarization and block China’s expansionist ambitions. Yet the race is far from over. As climate change reshapes the Arctic, the U.S. must continue investing in polar infrastructure, surveillance and alliances—or risk losing the high-stakes game for control of Earth’s last frontier. For now, the icebreakers are a crucial first move in a much larger geopolitical showdown. Final Thought: In the Arctic, ice is power—and America is finally arming itself for the fight. Sources for this article include: ZeroHedge.com DHS.gov FoxNews.comTrump threatens military action against Hamas over Gaza unrest, signaling policy shift
By Belle Carter // Share
Plandemic 2.0 on the RISE in China with Cattle Flu PATHOGEN outbreak
By S.D. Wells // Share
Trump insists Israel-Hamas ceasefire holds despite airstrikes and rising tensions
By Cassie B. // Share
U.S. escalates Caribbean strikes: Survivors reported in latest attack amid growing military buildup
By Belle Carter // Share
Mysterious high-altitude balloons spark surveillance concerns across U.S.
By Belle Carter // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share