Parler
Parler Gab
Gab
- China and Russia are using AI to enhance cyberattacks, including AI-generated disinformation, phishing scams and deepfake impersonations of officials, making attacks harder to detect. Microsoft blocked 1.6 million fake accounts per hour, highlighting the massive scale of the threat.
- Beijing's top targets include U.S. defense infrastructure, South China Sea disputes and critical national assets, aiming to steal military and economic secrets while disguising operatives as Americans online.
- Beyond Ukraine, Russia now targets NATO allies and small businesses aiding Kyiv, while Iran ramps up attacks on shipping firms to disrupt global trade.
- Hackers increasingly bypass security by recruiting insiders or stealing credentials, particularly in AI, quantum computing, biotech and defense sectors. Password attacks surged 30 percent in early 2024, accounting for 97 percent of identity breaches.
- Microsoft urges governments and businesses to adopt AI-driven security tools, improve employee training and proactively counter phishing/social engineering as cyber warfare becomes a strategic tool for hostile nations.
China's stealthy infiltration tactics
Microsoft uncovered a troubling trend: Chinese-linked operatives masquerading as Americans by listing U.S. locations, posting patriotic slogans and engaging in domestic political debates. These tactics suggest a coordinated effort to blend in while gathering intelligence or sowing discord. China's top cyber priorities include:- The South China Sea (amid territorial disputes with neighboring nations)
- The U.S. defense industrial base (seeking military and technological secrets)
- Critical infrastructure (potentially laying groundwork for disruptive attacks)
Sources include:
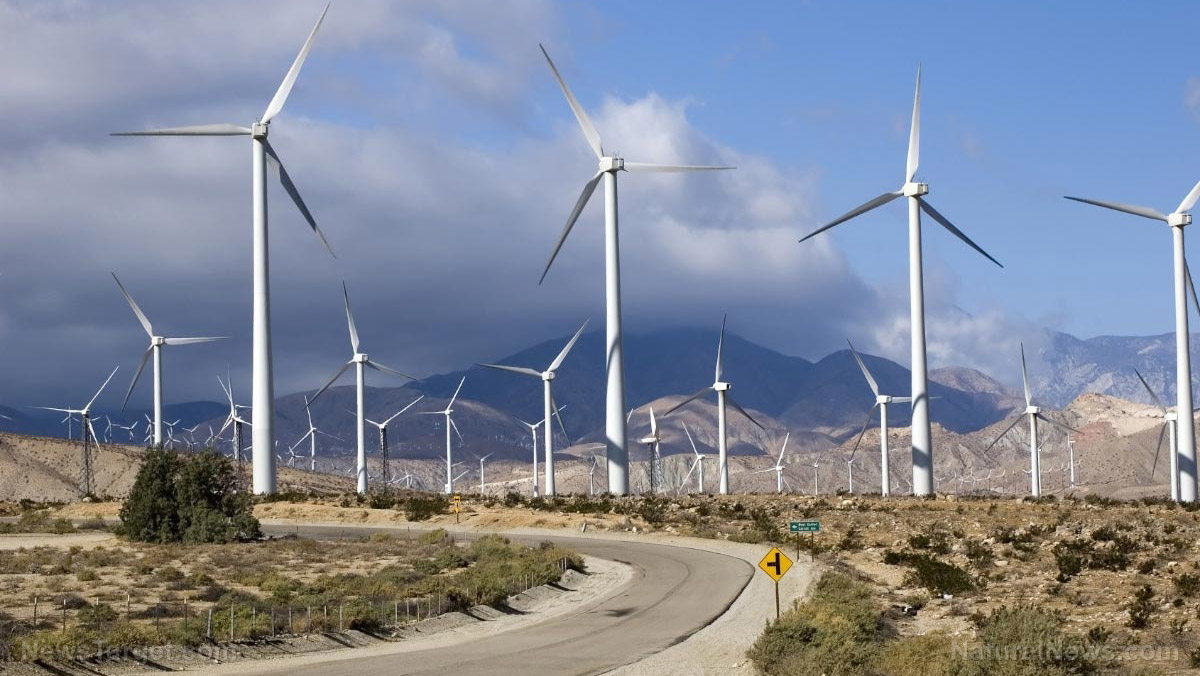
TheEpochTimes.com CDN-DynMedia-1.Microsoft.com BrightU.ai Brighteon.comWind energy’s hidden toll: New studies reveal devastating impact on bird and bat populations
By Kevin Hughes // Share
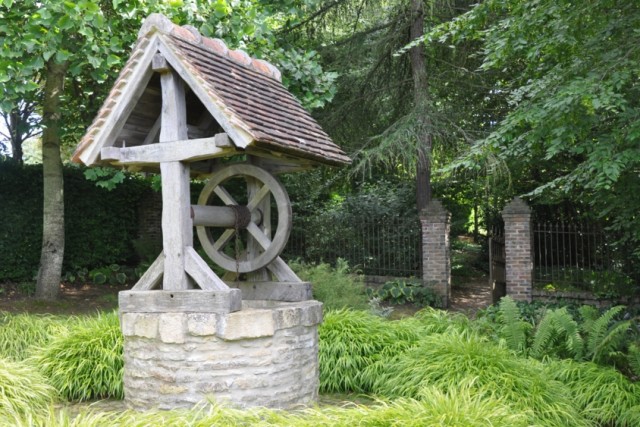
Water woes for Wisconsin homeowner expose a growing public health crisis
By Patrick Lewis // Share
The red screen of death: Google’s automated hit on a rival it couldn’t acquire
By Willow Tohi // Share
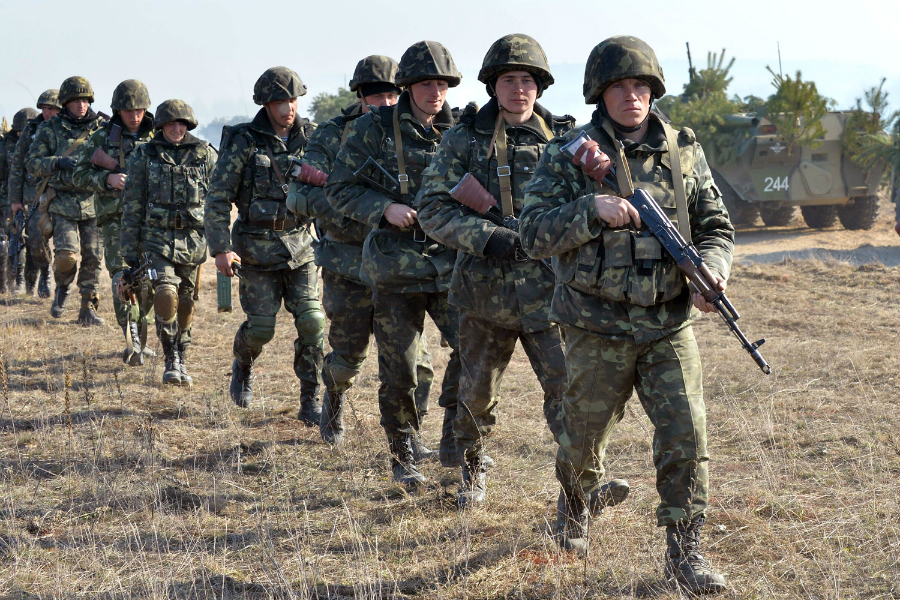
WWIII looms: U.S.-Russia standoff could escalate into global conflict
By Gregory Van Dyke // Share
The pendulum of doom: How El Niño-Southern Oscillation could transform into a climate catastrophe
By Belle Carter // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share